Aphthous ulcer
| Aphthous ulcer | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
 Mouth ulcer on the lower lip |
|
| ICD-10 | K12.0 |
| ICD-9 | 528.2 |
| MedlinePlus | 000998 |
| eMedicine | ent/700 derm/486 ped/2672 |
| MeSH | D013281 |
An aphthous ulcer (pronounced /ˈæpθəs/) also known as a canker sore, is a type of oral ulcer, which presents as a painful open sore inside the mouth[1] or upper throat characterized by a break in the mucous membrane. Its cause is unknown, but they are not contagious.[2] The condition is also known as aphthous stomatitis, and alternatively as Sutton's Disease, especially in the case of major, multiple, or recurring ulcers.
The term aphtha means ulcer; it has been used for many years to describe areas of ulceration on mucous membranes. Aphthous stomatitis is a condition which is characterized by recurrent discrete areas of ulceration which are almost always painful. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS) can be distinguished from other diseases with similar-appearing oral lesions, such as certain viral exanthems or herpes simplex, by their tendency to recur, and their multiplicity and chronicity. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is one of the most common oral conditions. At least 10% of the population has it, and women are more often affected than men. About 30–40% of patients with recurrent aphthae report a family history.[3]
Contents |
Classification
Aphthous ulcers are classified according to the diameter of the lesion.
Minor ulceration
"Minor aphthous ulcers" indicate that the lesion size is between 3 mm (0.1 in)-10 mm (0.4 in). The appearance of the lesion is that of an erythematous halo with yellowish or grayish color. Extreme pain is the obvious characteristic of the lesion. When the ulcer is white or grayish, the ulcer will be extremely painful and the affected lip may swell. They may last about 1 week.
Major ulcerations
Major aphthous ulcers have the same appearance as minor ulcerations, but are greater than 10 mm in diameter and are extremely painful. They usually take more than a month to heal, and frequently leave a scar. These typically develop after puberty with frequent recurrences. They occur on movable non-keratinizing oral surfaces, but the ulcer borders may extend onto keratinized surfaces. They may last about 10 to 14 days.
Herpetiform ulcerations
This is the most severe form. It occurs more frequently in females, and onset is often in adulthood. It is characterized by small, numerous, 1–3 mm lesions that form clusters. They typically heal in less than a month without scarring. Supportive treatment is almost always necessary.[4]
Signs and symptoms
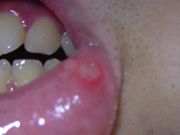
Aphthous ulcers usually begin with a tingling or burning sensation at the site of the future aphthous ulcer. In a few days, they often progress to form a red spot or bump, followed by an open ulcer.
The aphthous ulcer appears as a white or yellow oval with an inflamed red border. Sometimes a white circle or halo around the lesion can be observed. The gray-, white-, or yellow-colored area within the red boundary is due to the formation of layers of fibrin, a protein involved in the clotting of blood. The ulcer, which itself is often extremely painful, especially when agitated, may be accompanied by a painful swelling of the lymph nodes below the jaw, which can be mistaken for toothache; another symptom is fever. A sore on the gums may be accompanied by discomfort or pain in the teeth.
Causes
The exact cause of many aphthous ulcers is unknown but citrus fruits (e.g. oranges and lemons), physical trauma, stress, lack of sleep, sudden weight loss, food allergies, immune system reactions[5] and deficiencies in vitamin B12, iron, and folic acid[6] may contribute to their development. Nicorandil and certain types of chemotherapy are also linked to aphthous ulcers.[7]. One recent study showed a strong correlation with allergies to cow's milk [8]. Aphthous ulcers are a major manifestation of Behçet disease,[9] and are also common in people with Crohn's disease.[10]
Trauma to the mouth is the most common trigger.[11][12] Physical trauma, such as that caused by toothbrush abrasions, laceration with sharp or abrasive foods (such as toast, potato chips or other objects), accidental biting (particularly common with sharp canine teeth), after losing teeth, or dental braces can cause aphthous ulcers by breaking the mucous membrane. Other factors, such as chemical irritants or thermal injury, may also lead to the development of ulcers. Using a toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) may reduce the frequency of aphthous ulcers[13][14][15] but some studies have found no connection between SLS in toothpaste and aphthous ulcers.[16] Celiac disease has been suggested as a cause of aphthous ulcers; small studies of patients (33% or 1 out of 3) with Celiac disease did demonstrate a conclusive link between the disease and aphthous ulcers vs control group (23%)[17][18] but some patients benefited from eliminating gluten from their diet.[17]
There is no indication that aphthous ulcers are related to menstruation, pregnancy and menopause.[19] Smokers appear to be affected less often.[20]
Prevention
Oral and dental measures
- Regular use of non-alcoholic mouthwash may help prevent or reduce the frequency of sores. In fact, informal studies suggest that mouthwash may help to temporarily relieve pain.[21]
- In some cases, switching toothpastes can prevent aphthous ulcers from occurring with research looking at the role of sodium dodecyl sulfate (sometimes called sodium lauryl sulfate, or with the acronymes SDS or SLS), a detergent found in most toothpastes. Using toothpaste free of this compound has been found in several studies to help reduce the amount, size and recurrence of ulcers.[22][23][24]
- Dental braces are a common physical trauma that can lead to aphthous ulcers and the dental bracket can be covered with wax to reduce abrasion of the mucosa. Avoidance of other types of physical and chemical trauma will prevent some ulcers, but since such trauma is usually accidental, this type of prevention is not usually practical.
Nutritional therapy
- Zinc deficiency has been reported in people with recurrent aphthous ulcers.[25] The few small studies looking into the role of zinc supplementation have mostly reported positive results particularly for those people with deficiency,[26] although some research has found no therapeutic effect.[27]
Treatment
A number of different treatments exist for apthous ulcers including: analgesics, anesthetics agents, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory agents, steroids, sucralfate, tetracycline suspension, and silver nitrate.[28]
Amlexanox paste has been found to speed healing and improve pain.[29]
Vitamin B12 has been found to be effective in treating recurrent aphthous ulcers, regardless of whether there is a vitamin deficiency present.[30]
L-lysine can also be effective in treating aphthous ulcers.[31]
Suggestions to reduce the pain caused by an ulcer include: avoiding spicy food, rinsing with salt water or over-the-counter mouthwashes, proper oral hygiene and non-prescription local anesthetics.[32] Active ingredients in the latter generally include benzocaine,[33] benzydamine or choline salicylate.[34]
Anesthetic mouthwashes containing benzydamine hydrochloride have not been shown to reduce the number of new ulcers or significantly reduce pain,[35] and evidence supporting the use of other topical anesthetics is very limited though some individuals may find them effective.[36] In general their role is limited; their duration of effectiveness is generally short and does not provide pain control throughout the day; the medications may cause complications in children.[37]
Evidence is limited for the use of antimicrobial mouthwashes but suggests that they may reduce the painfulness and duration of ulcers and increase the number of days between ulcerations, without reducing the number of new ulcers.[38]
Milk of magnesia is useful against aphthous ulcers when used topically.[39]
Corticosteroid preparations containing hydrocortisone hemisuccinate or triamcinolone acetonide to control symptoms are effective in treating aphthous ulcers. [36][40][41]
The application of silver nitrate will cauterize the sore; a single treatment reduces pain but does not affect healing time.[42] though in children it can cause tooth discoloration if the teeth are still developing.[32] The use of tetracycline is controversial, as is treatment with levamisole, colchicine, gamma-globulin, dapsone, estrogen replacement and monoamine oxidase inhibitors.[33]
While commonly used, Magic mouthwash, a combination of a number of ingredients including viscous lidocaine, benzocaine, milk of magnesia, kaolin-pectate, chlorhexidine, or diphenhydramine, has little evidence to support its use in the treatment of aphthous ulcers.[29][43]
References
- ↑ aphthous ulcer at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "Mouth sores: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003059.htm. Retrieved 2010-05-31.
- ↑ Jurge S, Kuffer R, Scully C, Porter SR (2006). "Mucosal disease series. Number VI. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis". Oral Dis 12 (1): 1–21. doi:10.1111/j.1601-0825.2005.01143.x. PMID 16390463.
- ↑ Bruce AJ, Rogers RS (2003). "Acute oral ulcers". Dermatol Clin 21 (1): 1–15. doi:10.1016/S0733-8635(02)00064-5. PMID 12622264.
- ↑ Lewkowicz N, Lewkowicz P, Banasik M, Kurnatowska A, Tchorzewski H. (2005). "Predominance of Type 1 cytokines and decreased number of CD4(+)CD25(+high) T regulatory cells in peripheral blood of patients with recurrent aphthous ulcerations". Immunol Lett. 99 (1): 57–62. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2005.01.002. PMID 15894112.
- ↑ Wray D, Ferguson M, Hutcheon W, Dagg J (1978). "Nutritional deficiencies in recurrent aphthae". J Oral Pathol 7 (6): 418–23. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.1978.tb01612.x. PMID 105102.
- ↑ "Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma Cyberfamily — Side effects". NHL Cyberfamily. http://www.nhlcyberfamily.org/effects.htm. Retrieved August 10, 2006.
- ↑ Besu I, Jankovic L, Magdu IU, Konic-Ristic A, Raskovic S, Juranic Z. (2009). "Humoral immunity to cow's milk proteins and gliadin within the etiology of recurrent aphthous ulcers?". Oral Diseases 15 (8): 560–564. doi:10.1111/j.1601-0825.2009.01595.x. PMID 19563417.
- ↑ Internationalstudygroupforbehc (May 1990). "Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet's disease. International Study Group for Behçet's Disease". Lancet 335 (8697): 1078–80. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(90)92643-V. PMID 1970380.
- ↑ Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2007, Forty-Sixth Ed (2007), Edited by McPhee, SJ. MD, Papadakis, MA. MD and Tierney, LM, Jr., MD with Associate Authors – The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, New York, USA
- ↑ http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/40024908/][http://www.health-disease.org/skin-disorders/aphthous-ulcer.htm
- ↑ http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/bhcv2/bhcarticles.nsf/pages/Mouth_ulcers?OpenDocument
- ↑ Herlofson B, Barkvoll P (1994). "Sodium lauryl sulfate and recurrent aphthous ulcers. A preliminary study" (PDF). Acta Odontol Scand 52 (5): 257–9. doi:10.3109/00016359409029036. PMID 7825393. http://www.wealthpartners.net/pdf/0535.pdf.
- ↑ Herlofson B, Barkvoll P (1996). "The effect of two toothpaste detergents on the frequency of recurrent aphthous ulcers". Acta Odontol Scand 54 (3): 150–3. doi:10.3109/00016359609003515. PMID 8811135.
- ↑ Chahine L, Sempson N, Wagoner C (1997). "The effect of sodium lauryl sulfate on recurrent aphthous ulcers: a clinical study". Compend Contin Educ Dent 18 (12): 1238–40. PMID 9656847.
- ↑ Healy C, Paterson M, Joyston-Bechal S, Williams D, Thornhill M (1999). "The effect of a sodium lauryl sulfate-free dentifrice on patients with recurrent oral ulceration". Oral Dis 5 (1): 39–43. PMID 10218040.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Bucci P, Carile F, Sangianantoni A, D'Angio F, Santarelli A, Lo Muzio L. (2006). "Oral aphthous ulcers and dental enamel defects in children with celiac disease". Acta Paediatrica 95 (2): 203–7. doi:10.1080/08035250500355022. PMID 16449028.
- ↑ Sedghizadeh PP, Shuler CF, Allen CM, Beck FM, Kalmar JR. (2002). "Celiac disease and recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a report and review of the literature". Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radiology & Endodontics 94 (4): 474–8. doi:10.1067/moe.2002.127581. PMID 12374923.
- ↑ McCartan BE, Sullivan A: The association of menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause with recurrent oral aphthous stomatitis: a review and critique. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Sep;80(3 Pt 1):455-8. Review. PMID 1495706
- ↑ Tüzün B, Wolf R, Tüzün Y, Serdaroğlu S. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis and smoking. Int J Dermatol. 2000 May;39(5):358-60. PMID 10849126
- ↑ Studies mostly agree that antiseptic mouthwashes can help prevent recurrences:
* Meiller TF, Kutcher MJ, Overholser CD, Niehaus C, DePaola LG, Siegel MA (1991). "Effect of an antimicrobial mouthrinse on recurrent aphthous ulcerations". Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 72 (4): 425–9. doi:10.1016/0030-4220(91)90553-O. PMID 1923440.
* Skaare AB, Herlofson BB, Barkvoll P (1996). "Mouthrinses containing triclosan reduce the incidence of recurrent aphthous ulcers (RAU)". J. Clin. Periodontol. 23 (8): 778–81. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.1996.tb00609.x. PMID 8877665.
But this is not accepted by all reports:
* Barrons RW (2001). "Treatment strategies for recurrent oral aphthous ulcers". Am J Health Syst Pharm 58 (1): 41–50; quiz 51–3. PMID 11194135. - ↑ Herlofson BB, Barkvoll P (1996). "The effect of two toothpaste detergents on the frequency of recurrent aphthous ulcers". Acta Odontol. Scand. 54 (3): 150–3. doi:10.3109/00016359609003515. PMID 8811135.
- ↑ Chahine L, Sempson N, Wagoner C (1997). "The effect of sodium lauryl sulfate on recurrent aphthous ulcers: a clinical study". Compend Contin Educ Dent 18 (12): 1238–40. PMID 9656847.
- ↑ Healy CM, Paterson M, Joyston-Bechal S, Williams DM, Thornhill MH (1999). "The effect of a sodium lauryl sulfate-free dentifrice on patients with recurrent oral ulceration". Oral Dis 5 (1): 39–43. PMID 10218040.
- ↑ Wang SW, Li HK, He JS, Yin TA (1986). "[The trace element zinc and aphthosis. The determination of plasma zinc and the treatment of aphthosis with zinc] [The trace element zinc and aphthosis. The determination of plasma zinc and the treatment of aphthosis with zinc]" (in French). Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 87 (5): 339–43. PMID 3467416.
- ↑ Orbak R, Cicek Y, Tezel A, Dogru Y (2003). "Effects of zinc treatment in patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis". Dent Mater J 22 (1): 21–9. PMID 12790293.
- ↑ Wray D (1982). "A double-blind trial of systemic zinc sulfate in recurrent aphthous stomatitis". Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 53 (5): 469–72. doi:10.1016/0030-4220(82)90459-5. PMID 7048184.
- ↑ Altenburg A, Zouboulis CC (September 2008). "Current concepts in the treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis". Skin Therapy Lett. 13 (7): 1–4. PMID 18839042.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "data.memberclicks.com". http://data.memberclicks.com/site/fpin/770%20EBP%20-%20November%202009.pdf.
- ↑ Volkov I, Rudoy I, Freud T, et al (2009). "Effectiveness of vitamin B12 in treating recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". J Am Board Fam Med 22 (1): 9–16. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.01.080113. PMID 19124628.
- ↑ http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003059.htm
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Rauch, D. "Canker sores: Treatment". MedlinePlus. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000998.htm#Treatment. Retrieved May 8, 2008.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 ped/2672 at eMedicine
- ↑ "Aphthous Mouth Ulcers". Patient UK. February 2007. http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/23068855/. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ↑ "Aphthous ulcer – Evidence: Evidence on topical analgesics". Clinical Knowledge Summaries (Prodigy). National Library for Health. http://cks.library.nhs.uk/aphthous_ulcer/evidence/supporting_evidence/topical_analgesics#. Retrieved May 10, 2008.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Aphthous ulcer – Management". Clinical Knowledge Summaries (Prodigy). National Library for Health. http://cks.library.nhs.uk/aphthous_ulcer/management/detailed_answers/managing_aphthous_ulcers#. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ↑ "12.3.1 Drugs for oral ulceration and inflammation". British National Formulary for Children. British Medical Association, the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain , Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Neonatal and Paediatric Pharmacists Group. 2006. pp. 601–4.
- ↑ "Aphthous ulcer – Evidence: Evidence on antimicrobial mouthwash". Clinical Knowledge Summaries (Prodigy). National Library for Health. http://cks.library.nhs.uk/aphthous_ulcer/evidence/supporting_evidence/antimicrobial_mouthwash#. Retrieved May 10, 2008.
- ↑ Canker sores
- ↑ Scully C (July 2006). "Clinical practice. Aphthous ulceration". N. Engl. J. Med. 355 (2): 165–72. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp054630. PMID 16837680.
Commented in:
"Clinical review – aphthous ulceration". Medicines Information Web Site (Trent and West Midlands regional Medicines Information services). July 13, 2006. http://www.ukmicentral.nhs.uk/headline/database/printstory.asp?NewsID=5369. Retrieved May 9, 2008. - ↑ Scully C, Shotts R (July 2000). "ABC of oral health. Mouth ulcers and other causes of orofacial soreness and pain". BMJ 321 (7254): 162–5. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7254.162. PMID 10894697. PMC 1118165. http://www.bmj.com/cgi/content/full/321/7254/162.
- ↑ Alidaee MR, Taheri A, Mansoori P, Ghodsi SZ (September 2005). "Silver nitrate cautery in aphthous stomatitis: a randomized controlled trial". Br. J. Dermatol. 153 (3): 521–5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06490.x. PMID 16120136. http://dermatology.cdlib.org/DOJvol8num2/original/antibiotics2/jain.html.
- ↑ "Global Family Doctor - Wonca Online | Item search". http://www.globalfamilydoctor.com/search/GFDSearch.asp?itemNum=11439&ContType=HDA.
External links
- MayoClinic.com: Mouth Sores
- MayoClinic.com: Canker sore
- eMedicine: Canker Sores
- eMedicine: Aphthous Stomatitis
- Management of Aphthous Ulcers, American Family Physician
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||